The difference between SIS and DCS system
Emerson DCS
1.DCS is used for continuous measurement, conventional control (continuous, sequential, intermittent, etc.) and operation control management of the production process to ensure the smooth operation of the production device; SIS IS USED TO MONITOR the operation status of the production device, deal with the abnormal conditions quickly, minimize the harm, and keep the personnel and the production device in a safe state.
EMERSON DCS Card: 5X00226G02 I/O Interface Module
HIMA DCS Card:F8652X
2.DCS is a "dynamic" system, always continuous detection, operation and control of process variables, dynamic control of the production process, to ensure product quality and output; SIS is a "static" system, under normal working conditions, always monitor the operation of the production device, the system output is unchanged, no impact on the production process; In abnormal working conditions, according to the pre-designed logic calculation, so that the production device safety interlock or stop.
3.SIS is more stringent than DCS in terms of security, reliability and availability, so SIS and DCS hardware should be set independently in theory.

When designing an instrument safety system, the following basic principles must be followed
1. Reliability principles
System reliability refers to the probability of failure in a certain time interval. The reliability of the whole system is the product of the reliability of the components of the system. The decline of the reliability of any link will lead to the decline of the reliability of the whole system. People usually attach great importance to the reliability of logic control system, and often ignore the reliability of detection components and implementation components, which makes the reliability of the whole safety instrument system low and fails to meet the requirements of reducing the risk of controlled equipment. Reliability determines system security.
2. Usability principles
Availability (availability) refers to the probability that a repairable product will work properly at a certain time when it is used under specified conditions. The availability does not affect the security of the system, but the low availability of the system may lead to the failure of the device or plant to perform normal production.
For the cognitive process of the safety instrument system to the process, we should also pay attention to the availability of the system, correctly judge the process accident, try to reduce the abnormal shutdown of the device, reduce the economic loss caused by the opening and shutdown.
3. Fail-safe principles
The fail-safe principle refers to that when the SIS fails due to internal or external reasons, the protected object (device) should be safely stopped in a predetermined order and automatically transferred to a safe state. Specifically reflected as:
(1) Normally closed contact is selected for the field switch instrument. When the process is normal, the contact is closed. When the safety limit is reached, the contact is disconnected and the interlocking action is triggered.
(2) the solenoid valve adopts normal excitation, interlocking is not moved, solenoid valve coil charged, interlocking action when the power.
(3) The contacts sent to the electrical distribution room for starting/stopping the motor shall be isolated by intermediate relays, and the excitation circuit shall be fault-safe.
(4) As a control device, "fail-safe" means that it should at least interlock when its own failure occurs rather than when the process or equipment exceeds its limit. In order to safely stop in a predetermined sequence (which is safe for the process and equipment), and then through hardware and software redundancy and fault tolerance techniques, faults are detected within a process safe time, and error correction procedures are automatically executed to troubleshoot the faults.
4. Principle of process adaptation
The safety instrument system must be set according to the operation law of the process, and serve for the normal operation and abnormal operation of the process. In normal time, the safety instrument system can not affect the process operation. In the process of dangerous situation, the safety instrument system should play a role to ensure the safety of the process device. This is the process adaptation principle of system design.
5. The principle of independent Settings
The so-called independent setting principle means that the whole SIS system should be independent of the process control system (such as DCS), so as to reduce the probability of simultaneous failure of control function and safety function, so that it can independently complete the safety function of automatic protection interlock without being attached to the process control system. The unit requiring independent setting shall have detection element, actuator element, logic operation element and communication equipment. A complex SIS should be reasonably divided into multiple subsystems, each subsystem should be relatively independent, and the backup manual function should be set up in groups.
6. The principle of least intermediate links
SIS intermediates should be minimal. The more instruments in a loop, the worse the reliability, typically in the case of intrinsically safe loop applications. Therefore, the flameproof instrument can be used as far as possible to reduce the fault source caused by the safety grid and reduce the false stop.
7. Principle of redundancy
For measuring instrument, SIL1 level safety instrument function, can use a single measuring instrument; SIL2 safety meter function, it is advisable to use redundant measuring instruments; SIL3 safety meter function, should use redundant measuring instruments; When high security is required, the "or" logic structure should be adopted. When high availability is required, the logical structure of "and" should be adopted. When both security and availability need to be guaranteed, the logical structure of "three take two" should be adopted.
Single control valve is available for SIL1 level safety meter function for final components; SIL2 safety meter function, should use redundant control valve; SIL3 safety meter function, should use redundant control valve; Can use 1 regulating valve and 1 cut off valve, can also use 2 cut off valve. The redundant setting of the control valve does not mean that the redundant setting corresponds to the safety integrity level. If the control valve cannot be configured redundantly, a single control valve is used, but the supporting solenoid valve should be configured redundantly. The solenoid valve of safety instrument system should preferentially choose high temperature insulation coil, long - term electrified type, flameproof type. In the process of normal operation, the solenoid valve should be excited (live); In the process of abnormal operation, the solenoid valve non-excitation (loss of power).
For logic controller, SIL1 safety meter function, it is advisable to use redundant logic controller; SIL2 safety meter function, should use redundant logic controller; SIL3 safety meter function, must use redundant logic controller.
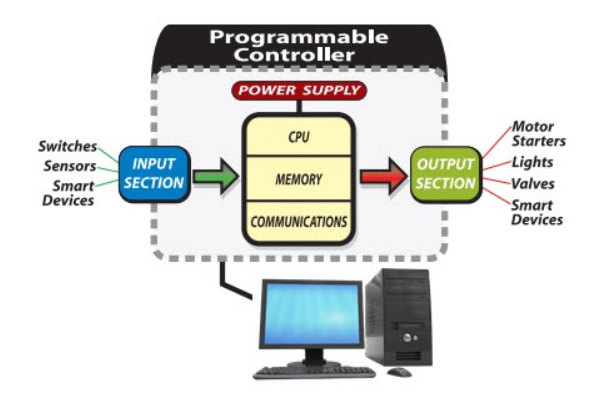
More...